Laboratory
Use this module to control the laboratory equipment.
>>> import opticomlib.lab as lab
>>> lab.search_inst()
('ASRL3::INSTR', 'ASRL4::INSTR', 'USB::0x0699::0x3130::9211219::INSTR')
Functions
Intruments search |
|
|
Instrument connection Connect to an instrument via VISA. |
List available serial ports and print their descriptions. |
|
|
Signal Synchronizer |
|
Eye diagram parameters v2 |
|
Saves measurement data of signals in an HDF5 file. |
|
Loads all datasets and metadata from an HDF5 file in a generic way. |
Classes
|
Tektronix Programmable Pattern Generator PPG3204 |
|
Tektronix PED3200 / PED4000 Series Programmable Error Detector |
|
Minimal SCPI driver for IDPhotonics lasers |
|
LeCroy Wave Expert 100H - minimal, extensible VISA wrapper for Teledyne LeCroy MAUI/XStreamDSO scopes adquisition. |
|
Driver for EXFO FVA-60B Variable Attenuator. |
- opticomlib.lab.search_inst()[source]
Intruments search
Search for the available instruments in the system and print the IDs.
- opticomlib.lab.connect_inst(addr_ID: str)[source]
Instrument connection Connect to an instrument via VISA. :param addr_ID: VISA resource of the instrument (e.g. ‘USB::0x0699::0x3130::9211219::INSTR’). :type addr_ID:
str- Returns:
inst – A connection (session) to the instrument.
- Return type:
visa.Resource
- opticomlib.lab.list_serial_ports()[source]
List available serial ports and print their descriptions.
Uses serial.tools.list_ports.comports() to discover serial ports. Prints “Ports not found” when no ports are found, otherwise prints the .description for each discovered port.
- opticomlib.lab.SYNC(signal_rx: electrical_signal | ndarray, slots_tx: binary_sequence | ndarray, sps: int = None)[source]
Signal Synchronizer
Synchronizes the received signal with the transmitted signal to determine the starting position in the received signal for further processing. This is done by performing a correlation between the received signal and the transmitted signal and finding the maximum correlation position and shifting the received signal to that position (deleting the samples before the maximum correlation position).
- Parameters:
signal_rx (
electrical_signal|np.ndarray) – The received digital signal (from the oscilloscope or an ADC).slots_tx (
binary_sequence|np.ndarray) – The transmitted slots sequence.sps (
int, optional) – Number of samples per slot of the digitalized signalsignal_rx.
- Returns:
A tuple containing the synchronized digital signal and the position in the
signal_rxarray from which synchronization was performed.- Return type:
tuple[electrical_signal,int]- Raises:
TypeError – The
spsmust be an integer to perform synchronization.BufferError – If the number of received slots have to be greater than the transmitted slots.
ValueError – If no correlation maximum is found.
- opticomlib.lab.GET_EYE_v2(sync_signal: electrical_signal | ndarray, slots_tx: binary_sequence | ndarray, nslots: int = 4096)[source]
Eye diagram parameters v2
Estimate the means and standard deviations of levels 0 and 1 in the
sync_signalby knowing the transmitted sequenceslots_tx. It separates the received signal levels corresponding to transmitted level 0 and 1 and estimates the means and standard deviations, different todevices.GET_EYE()that assume transmitted bits are not known.- Parameters:
sync_signal (electrical_signal) – Synchronized digital signal in time with the transmitted signal.
slots_tx (binary_sequence) – Transmitted bit sequence.
nslots (int, default: 8192) – Number of slots to use for estimation.
- Returns:
A dictionary containing the following keys:
sps: Samples per slot of the digital signal.y: Synchronized digital signal.unos: Received signal levels corresponding to transmitted level 1.zeros: Received signal levels corresponding to transmitted level 0.t0: Time instants for level 0.t1: Time instants for level 1.i: Position in the ‘signal’ vector from which synchronization was performed.mu0: Mean of level 0.mu1: Mean of level 1.s0: Standard deviation of level 0.s1: Standard deviation of level 1.
- Return type:
dict
- opticomlib.lab.save_h5(filename, **datos)[source]
Saves measurement data of signals in an HDF5 file.
This function creates an HDF5 file that contains the common time vector, wavelengths, signal data matrix and optional metadata from the oscilloscope and experiment setup.
- Parameters:
filename (str) – Base name of the file (without extension). ‘.h5’ will be added.
**datos (dict) – Name and value of the parameter to save. For example save_h5(‘name’, time=t, wavelength=w)
- opticomlib.lab.load_h5(filename)[source]
Loads all datasets and metadata from an HDF5 file in a generic way.
This function reads an HDF5 file and returns a dictionary with all datasets found (arrays loaded into memory) and metadata if they exist.
- Parameters:
filename (str) – Base name of the file (without extension). ‘.h5’ will be added.
- Returns:
data – Dictionary with dataset names as keys and ndarray values. If a ‘metadata’ group exists, includes a ‘metadata’ key with dict of attributes.
- Return type:
dict
- class opticomlib.lab.PPG3204(addr_ID: str = None, reset: bool = True)[source]
Tektronix Programmable Pattern Generator PPG3204
The PPG3204 is a Programmable Pattern Generator. It is a 4-channel pattern generator with 32 Gb/s maximum data rate. This class provides a set of methods to control the PPG3204.
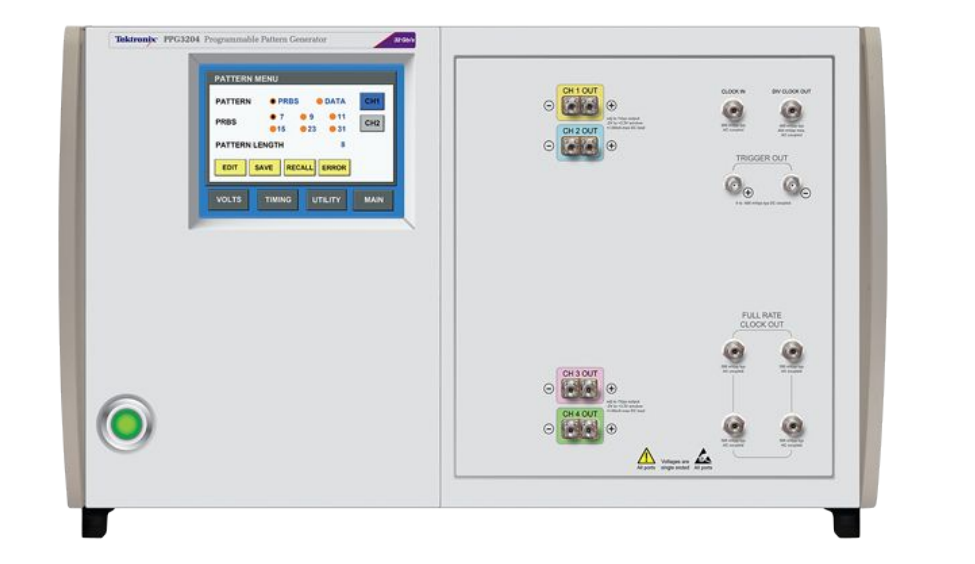
The PPG3204 has the following features:
Attributes
A connection (session) to the PPG instrument (if addr_ID is provided).
Number of channels of the PPG3204, 4 channels.
Pattern length minimum value, 2 bit.
Pattern length maximum value, 2^21 = 2097152 (2M) bits.
Minimum amplitude of the output signal, 0.3 V.
Maximum amplitude of the output signal, 2 V.
Minimum offset of the output signal, -2 V.
Maximum offset of the output signal, 3 V.
Minimum frequency, 1.5 GHz.
Maximum frequency, 32 GHz.
Mode of the pattern generator, ['DATA', 'PRBS']
The order of polynomial generator for PRBS_TYPE, [7,9,11,15,23,31]
Maximum length of the memory of the PPG3204, 2^21 = 2097152 (2M) for each channel.
Maximum length of the data to send in a single command, 1024 bits.
Minimum skew, -25 ps
Maximum skew, 25 ps
Methods
__init__([addr_ID, reset])Initialize the PPG3204.
__call__([data_rate, patt_len, amplitude, ...])Configure the PPG3204 with the specified parameters for specified channels.
reset()Reset the PPG to its default state.
patt_len(length[, CHs])Set Data Pattern Length (only relevant if type is DATA).
get_patt_len([CHs])Get the current length of pattern for specified channels
patt_type(type[, CHs])Set pattern type (DATA or PRBS).
get_patt_type([CHs])Get patt_type of the PPG3204 for each channels specified, can be 'DATA' or 'PRBS'
prbs(order[, CHs])Set the order of polynomial generator for PRBS patt_type.
get_prbs([CHs])Get the prbs polynomial order for each channel specified
data(data[, start_addr, CHs])Set the data of the pattern.
get_data(size[, start_addr, CHs])Get the data of the pattern for each specified channel
bits_shift(bsh[, CHs])Set the bits shift of the pattern
get_bits_shift([CHs])Get the bits shift of the pattern for each specified channel
output(state[, CHs])Enable or disable the output of the channels
get_output([CHs])Get the output state of the channels
data_rate(value)Set the bit rate of the pattern
Get the frequency of the pattern.
skew(skew[, CHs])Set the skew of the channels
get_skew([CHs])Get the skew of the channels
amplitude(value[, CHs])Set the peak-to-peak output voltage (in mV).
get_amplitude([CHs])Get the peak-to-peak output voltage (in mV).
offset(value[, CHs])Set offset voltage (in mV)
get_offset([CHs])Get the offset voltage (in mV)
setup([data_rate, patt_type, patt_len, ...])Configure the PPG3204 with the specified parameters for specified channels.
get_metadata([ch])Retrieve a summary of the current PPG configuration for the specified channel as a dictionary.
print_setup([ch])Print the current configuration of the PPG3204 for a specified channel.
- CHANNELS = 4
Number of channels of the PPG3204, 4 channels.
- PATT_LEN_MIN = 2
Pattern length minimum value, 2 bit.
- PATT_LEN_MAX = 2097152
Pattern length maximum value, 2^21 = 2097152 (2M) bits.
- AMPLITUDE_MIN = 0.3
Minimum amplitude of the output signal, 0.3 V.
- AMPLITUDE_MAX = 2
Maximum amplitude of the output signal, 2 V.
- OFFSET_MIN = -2
Minimum offset of the output signal, -2 V.
- OFFSET_MAX = 3
Maximum offset of the output signal, 3 V.
- FREQ_MIN = 1500000000.0
Minimum frequency, 1.5 GHz.
- FREQ_MAX = 32000000000.0
Maximum frequency, 32 GHz.
- PATT_TYPE = ['DATA', 'PRBS']
Mode of the pattern generator, [‘DATA’, ‘PRBS’]
- PRBS_ORDERS = [7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31]
The order of polynomial generator for PRBS_TYPE, [7,9,11,15,23,31]
- MAX_MEMORY_LEN = 2097152
Maximum length of the memory of the PPG3204, 2^21 = 2097152 (2M) for each channel.
- MAX_CHUNK_LEN = 1024
Maximum length of the data to send in a single command, 1024 bits.
- MIN_SKEW = -2.5e-11
Minimum skew, -25 ps
- MAX_SKEW = 2.5e-11
Maximum skew, 25 ps
- __init__(addr_ID: str = None, reset: bool = True)[source]
Initialize the PPG3204.
If
addr_IDis not passed as argument, methods will print the commands instead of sending them to the PPG. This is useful for debugging.- Parameters:
addr_ID (
str, optional) – VISA resource of the PPG (e.g. ‘USB::0x0699::0x3130::9211219::INSTR’). Default is None.
- inst
A connection (session) to the PPG instrument (if addr_ID is provided).
- patt_len(length: int, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set Data Pattern Length (only relevant if type is DATA).
- get_patt_len(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the current length of pattern for specified channels
- patt_type(type: Literal['DATA', 'PRBS'], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set pattern type (DATA or PRBS).
- Parameters:
type (str) – ‘DATA’ or ‘PRBS’.
CHs (int or list) – Channels to configure.
- get_patt_type(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get patt_type of the PPG3204 for each channels specified, can be ‘DATA’ or ‘PRBS’
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the patt_type.- Returns:
patt_type – Every channel patt_type.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- prbs(order: Literal[7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set the order of polynomial generator for PRBS patt_type.
- Parameters:
order (
intorArray_Like(int)) – order of the polynomial generator. Default7CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to set the order.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
orderis not in the correct format.
Notes
PRBS pattern lengths Independently selected for each channel.
\(2^7-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^7 + X^6 + 1\)
\(2^9-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^9 + X^5 + 1\)
\(2^{11}-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^{11} + X^9 + 1\)
\(2^{15}-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^{15} + X^{14} + 1\)
\(2^{23}-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^{23} + X^{18} + 1\)
\(2^{31}-1\) bits. Polynomial \(= X^{31} + X^{28} + 1\)
- get_prbs(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the prbs polynomial order for each channel specified
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the order.- Returns:
order – Every channel order.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- data(data: str | ndarray, start_addr: int = 1, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set the data of the pattern.
Programs the pattern data memory. Each byte of pattern data is a character (0 or 1) representing one bit of pattern data. The start address can be any bit location from 1 to MAX_MEMORY_LEN. MAX_MEMORY_LEN is \(2^{21} = 2097152\) (2M) for each channel.
- Parameters:
data (
strorArray_Like(int)) – Data to set to the specified channels.start_addr (
int, optional) – Start address of the data to set in the pattern memory. The range is from 1 to 2^21. Default1.CHs (
intorArray_Like, optional) – Channels to set the data. IfCHs=Nonedata will be fixed in all channels.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
datais not in the correct format.- Warns:
UserWarning – If the length of the data is out of the range of the PPG3204.
Examples
In this examples we don’t pass the argument
addr_IDin order to print the commands output. For communication with a device this parameter is requered.>>> from opticomlib.lab import PPG3204 >>> >>> ppg = PPG3204() >>> >>> ppg.set_data('000111000111', CHs=2) :DIG2:PATT:DATA 1,12,#212000111000111 >>> >>> ppg.set_data('000111000111') :DIG1:PATT:DATA 1,12,#212000111000111 :DIG2:PATT:DATA 1,12,#212000111000111 :DIG3:PATT:DATA 1,12,#212000111000111 :DIG4:PATT:DATA 1,12,#212000111000111 >>> >>> ppg.set_data([[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1]], CHs=[3,4]) :DIG3:PATT:DATA 1,4,#141010 :DIG4:PATT:DATA 1,4,#140101
- get_data(size: int, start_addr: int = 1, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the data of the pattern for each specified channel
- Parameters:
size (
int) – Size of the data to get from the pattern memory.start_addr (
int, optional) – Start address of the data to get from the pattern memory. The range is from 1 to 2^21. Default is 1.CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the data.
- Returns:
data – Data of the pattern for each channel.
- Return type:
np.ndarray, shape (n_channels, n_bits)- Warns:
UserWarning – If the start address or the size is out of the range of the PPG3204.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
start_addrorsizeare not integers.
- bits_shift(bsh: int, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set the bits shift of the pattern
- Parameters:
bsh (
intorArray_Like(int)) – Bits shift to set to the specify channels.CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the bits shift. IfCHs=Nonebits shift will be fixed in all channels.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
bshis not in the correct format.
Notes
- Pattern shift advance or delay. This is equivalent to unlimited shifting since this range allow shifting the longest pattern to any position.
Range: \(\pm(2^{30}-1)\)
Resolution: 1 bit
- get_bits_shift(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the bits shift of the pattern for each specified channel
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the bits shift.- Returns:
bsh – Every channel bits shift.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- output(state: Literal[0, 1, 'ON', 'OFF'], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Enable or disable the output of the channels
- Parameters:
state (
int{0, 1} orstr{‘ON’, ‘OFF’}) – State to set for the channels (‘ON’ to enable, ‘OFF’ to disable).CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the output state. IfCHs=Noneall channels will be affected.
- get_output(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the output state of the channels
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to get the output state. IfCHs=Noneall channels will be queried.- Returns:
state – Every channel output state (‘ON’ or ‘OFF’).
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- data_rate(value: float)[source]
Set the bit rate of the pattern
Range: 1.5 GHz to 32 GHz
Resolution: 10 kb/s
Accuracy: \(\pm 5\) ppm
- Parameters:
value (
float) – Bit Rate of the pattern in bits/s.
- get_data_rate()[source]
Get the frequency of the pattern.
- Returns:
freq – Bit Rate of the pattern in bits/s.
- Return type:
float
- skew(skew: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set the skew of the channels
The channel skew is the timing of the data output.
Range: -25 to 25 ps
Resolution: 0.1 ps
- Parameters:
skew (
floatorArray_Like(float)) – Skew to set to the specify channelsCHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the skew. IfCHs=Noneskew will be fixed in all channels.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
skewis not in the correct format.
- get_skew(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the skew of the channels
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the skew.- Returns:
skew – Every channel skew.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- amplitude(value: float | list[float], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set the peak-to-peak output voltage (in mV).
- Parameters:
value (
floatorArray_Like) – Amplitude to set to the specify channelsCHs (
intorArray_Like, optional) – Channels to set the amplitude. IfCHs=Noneamplitude will be fixed in all channels.
- get_amplitude(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the peak-to-peak output voltage (in mV).
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the amplitude.- Returns:
Vout – Every channel output voltage.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- offset(value: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set offset voltage (in mV)
- Parameters:
value (
floatorArray_Like(float)) – Offset to set to the specify channelsCHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the offset. IfCHs=Noneoffset will be fixed in all channels.
- Raises:
ValueError – If
valueis not in the correct format.- Warns:
UserWarning – If the offset is out of the range of the PPG3204.
Notes
- Offset adjust relative to nominal position.
Range: -2000 to 3000 mV
- get_offset(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the offset voltage (in mV)
- Parameters:
CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – List of channels to get the offset.- Returns:
offset – Every channel offset.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- __call__(data_rate: float = None, patt_len: int | list[int] = None, amplitude: float | list[float] = None, offset: float | list[float] = None, bsh: int | list[int] = None, skew: float | list[float] = None, patt_type: Literal['DATA', 'PRBS'] = None, prbs: int | list[int] = None, data: ndarray | list[numpy.ndarray] = None, output: Literal[0, 1, 'ON', 'OFF'] = None, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Configure the PPG3204 with the specified parameters for specified channels.
- Parameters:
data_rate (
float, optional) – Frequency of the pattern in Hz. The range is from 1.5 GHz to 32 GHz.patt_len (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Pattern length for every channel specified inCHs.amplitude (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Amplitude to set to the specify channelsoffset (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Offset to set to the specify channelsbsh (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Bits shift to set to the specify channelsskew (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Skew to set to the specify channelspatt_type (
str, optional) – Work patt_type of the PPG,"DATA"or`"PRBS". Default"PRBS"prbs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – order of the polynomial generator. Ifpatt_type='PRBS'.data (
np.ndarrayorArray_Like(np.ndarray), optional) – Data to set to the specify channels. Ifpatt_type='DATA'.CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the configuration.
Examples
In this examples we don’t pass the argument
addr_IDin order to print the commands output. For communication with a device this parameter is required.>>> from opticomlib.lab import PPG3204 >>> >>> ppg = PPG3204() >>> ppg(data_rate=10e9, patt_len=1000, amplitude=1.5, offset=0.5, bsh=10, skew=0.5e-12, patt_type='PRBS', prbs=7, CHs=2) :FREQ 1.0e+10 :DIG2:PATT:LENG 1000 :VOLT2:POS 1.5v :VOLT2:POS:OFFS 0.5v :DIG2:PATT:BSH 10 :SKEW2 5e-13 :DIG2:PATT:TYPE PRBS :DIG2:PATT:PLEN 7
- get_metadata(ch: int = 1)[source]
Retrieve a summary of the current PPG configuration for the specified channel as a dictionary.
- print_setup(ch: int = None)[source]
Print the current configuration of the PPG3204 for a specified channel.
- setup(data_rate: float = None, patt_type: Literal['DATA', 'PRBS'] = None, patt_len: int | list[int] = None, amplitude: float | list[float] = None, offset: float | list[float] = None, bsh: int | list[int] = None, skew: float | list[float] = None, prbs: int | list[int] = None, data: ndarray | list[numpy.ndarray] = None, output: Literal[0, 1, 'ON', 'OFF'] = None, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Configure the PPG3204 with the specified parameters for specified channels.
- Parameters:
data_rate (
float, optional) – Frequency of the pattern in Hz. The range is from 1.5 GHz to 32 GHz.patt_len (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Pattern length for every channel specified inCHs.amplitude (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Amplitude to set to the specify channelsoffset (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Offset to set to the specify channelsbsh (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Bits shift to set to the specify channelsskew (
floatorArray_Like(float), optional) – Skew to set to the specify channelspatt_type (
str, optional) – Work patt_type of the PPG.prbs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – order of the polynomial generator. Ifpatt_type='PRBS'.data (
np.ndarrayorArray_Like(np.ndarray), optional) – Data to set to the specify channels. Ifpatt_type='DATA'.CHs (
intorArray_Like(int), optional) – Channels to set the configuration.
Examples
In this examples we don’t pass the argument
addr_IDin order to print the commands output. For communication with a device this parameter is required.>>> from opticomlib.lab import PPG3204 >>> >>> ppg = PPG3204() >>> ppg(data_rate=10e9, patt_len=1000, amplitude=1.5, offset=0.5, bsh=10, skew=0.5e-12, patt_type='PRBS', prbs=7, CHs=2) :FREQ 1.0e+10 :DIG2:PATT:LENG 1000 :VOLT2:POS 1.5v :VOLT2:POS:OFFS 0.5v :DIG2:PATT:BSH 10 :SKEW2 5e-13 :DIG2:PATT:TYPE PRBS :DIG2:PATT:PLEN 7
- class opticomlib.lab.PED4002(addr_ID: str = None, reset: bool = True)[source]
Tektronix PED3200 / PED4000 Series Programmable Error Detector
High-performance programmable error detector (up to 32 Gb/s for PED3200, 40 Gb/s for PED4000). This class mirrors the remote programming command set described in the user manual PED3200-PED4000-Programmable-Error-Detector-User-Manual-077109501.pdf.
Attributes
instMaximum number of channels (Model dependent).
Pattern length minimum value.
Pattern length maximum value for single channel config (4 Mbit).
Pattern length maximum value per channel for 2-ch config (2 Mbit).
Minimum clock delay (-50 ps).
Maximum clock delay (+50 ps).
Minimum Eye Edge BER Threshold.
Maximum Eye Edge BER Threshold.
Minimum Synchronization BER Threshold.
Maximum Synchronization BER Threshold.
Mode of the error detector.
Supported PRBS polynomial orders.
Maximum length of the data block to write in a single command.
Main methods
__init__([addr_ID, reset])Initialize the PED.
__call__(*args, **kwargs)Call self as a function.
reset()Reset the PED to default settings (
*RST).patt_len(length[, CHs])Set Data Pattern Length (only relevant if type is DATA).
get_patt_len([CHs])Get the current length of pattern for specified channels
patt_type(type[, CHs])Set pattern type (DATA or PRBS).
get_patt_type([CHs])Get current pattern type.
prbs(order[, CHs])Set PRBS Polynomial order (2^N - 1).
get_prbs([CHs])Get current PRBS order.
data(data[, start_addr, CHs])Program the user pattern data.
get_data(length[, start_addr, CHs])Retrieve binary pattern data as numpy bool array.
sync([CHs, wait])Initiate pattern synchronization.
is_sync([CHs])Check if the specified channels are synchronized.
sync_threshold(ber[, CHs])Programs the synchronization BER threshold.
get_sync_threshold([CHs])Get current synchronization BER threshold.
center_offset([CHs, wait])Initiates the center offset process.
offset(offset[, CHs])Set decision threshold offset (in mV).
get_offset([CHs])Get current decision threshold offset (in mV).
get_voltage_edges([CHs])Get Eye Voltage Edges (in Volts).
center_delay([CHs, wait])Initiates the center clock delay process.
delay(delay[, CHs])Set Clock to Data delay (in ps).
get_delay([CHs])Get current Clock to Data delay (in picoseconds).
get_time_edges([CHs])Get Eye Time Edges (in secons).
eye_threshold(ber[, CHs])Set Eye Edge BER Threshold.
get_eye_threshold([CHs])Get current Eye Edge BER Threshold.
is_running([CHs])Check if error detection is running (gating enabled).
run([CHs])Start error detection (enable gating).
stop([CHs])Stop error detection (disable gating).
get_ber([CHs])Get current Bit Error Ratio.
get_error_count([CHs])Get total error count.
get_bit_count([CHs])Get total bit count.
get_frequency([CHs])Queries the frequency measured at the clock input.
setup([patt_type, patt_len, prbs, data, ...])Configure the PED with the specified parameters in a sequential and logical order.
get_metadata([ch])Retrieve a summary of the current PED configuration for the specified channel as a dictionary.
print_setup([ch])Print a summary of the current PED configuration for the specified channel.
- CHANNELS = 2
Maximum number of channels (Model dependent).
- PATT_LEN_MIN = 2
Pattern length minimum value.
- PATT_LEN_MAX_1CH = 4194304
Pattern length maximum value for single channel config (4 Mbit).
- PATT_LEN_MAX_2CH = 2097152
Pattern length maximum value per channel for 2-ch config (2 Mbit).
- CLK_DELAY_MIN = -50
Minimum clock delay (-50 ps).
- CLK_DELAY_MAX = 50
Maximum clock delay (+50 ps).
- EYE_THRESH_MIN = 1e-11
Minimum Eye Edge BER Threshold.
- EYE_THRESH_MAX = 0.1
Maximum Eye Edge BER Threshold.
- SYNC_THRESH_MIN = 1e-08
Minimum Synchronization BER Threshold.
- SYNC_THRESH_MAX = 0.1
Maximum Synchronization BER Threshold.
- PATT_TYPE = ['DATA', 'PRBS']
Mode of the error detector.
- PRBS_ORDERS = [7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31]
Supported PRBS polynomial orders.
- MAX_CHUNK_LEN = 1024
Maximum length of the data block to write in a single command.
- __init__(addr_ID: str = None, reset: bool = True)[source]
Initialize the PED.
- Parameters:
addr_ID (
str, optional) – VISA resource of the PED. Default is None (Debug mode).reset (
bool, optional) – If True, reset the instrument to factory defaults upon connection. Default is True.
- patt_len(length: int, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set Data Pattern Length (only relevant if type is DATA).
- get_patt_len(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get the current length of pattern for specified channels
- patt_type(type: Literal['DATA', 'PRBS'], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set pattern type (DATA or PRBS).
- Parameters:
type (str) – ‘DATA’ or ‘PRBS’.
CHs (int or list) – Channels to configure.
- prbs(order: Literal[7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31], CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set PRBS Polynomial order (2^N - 1).
- Parameters:
order (int) – One of [7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31].
- data(data: str | ndarray, start_addr: int = 1, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Program the user pattern data.
- Parameters:
data (str or array) – The binary data (e.g. “010110”).
start_addr (int) – Memory start address (1-based).
CHs (int or list) – Channels to program.
- get_data(length: int, start_addr: int = 1, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Retrieve binary pattern data as numpy bool array.
- sync_threshold(ber: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Programs the synchronization BER threshold. This is the maximum BER value for which a synchronization is considered successful. Also, in auto sync mode, the current BER is monitored and compared to this threshold. The threshold may range from 10-1 to 10-8 in decade steps. Synchronization will succeed only if the BER of the system is less than the sync BER threshold.
- Parameters:
ber (float) – BER threshold between 1e-8 and 1e-1.
CHs (int or list) – Channels to configure.
- center_offset(CHs: int | list[int] = None, wait=True)[source]
Initiates the center offset process.
The center offset process can take a significant amount of time. It uses the EYE EDGE BER THRESHOLD to determine the eye edges during the process. Lower EYE EDGE BER THRESHOLD values take more time, as do data patterns (vs PRBS) and longer data pattern lengths.
- offset(offset: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set decision threshold offset (in mV). Range -300 mV to +300 mV.
Programs the data offset voltage. The default value of 0 is normally good for 50% duty input signals.
- center_delay(CHs: int | list[int] = None, wait=True)[source]
Initiates the center clock delay process.
The center clock delay process can take a significant amount of time. It uses the EYE EDGE BER THRESHOLD to determine the eye edges during the process. Lower EYE EDGE BER THRESHOLD values take more time, as do data patterns (vs PRBS) and longer data pattern lengths.
- delay(delay: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set Clock to Data delay (in ps).
Range: +/- 50 ps.
- get_time_edges(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get Eye Time Edges (in secons).
Queries the left or right (time axis) eye edges as determined during the most recent automatic process that sets the horizontal sampling point. This includes the Center Clock Delay and Auto Align processes. If those processes have not been run or failed on the most recent attempt, the return value will be 9.91e37. (NaN)
- eye_threshold(ber: float, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Set Eye Edge BER Threshold.
Programs the eye edge BER threshold. This is the maximum BER value for which an eye edge is considered valid during automatic processes that determine eye edges. The threshold may range from 10-1 to 10-11 in decade steps.
- get_voltage_edges(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get Eye Voltage Edges (in Volts).
Queries the upper and lower (voltage axis) eye edges as determined during the most recent automatic process that sets the vertical sampling point. This includes the Center Offset and Auto Align processes. If those processes have not been run or failed on the most recent attempt, the return value will be 9.91e37. (NaN)
- is_running(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Check if error detection is running (gating enabled).
- get_ber(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Get current Bit Error Ratio.
Returns NaN if not synced or valid.
- get_frequency(CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Queries the frequency measured at the clock input.
This value is valid only if the error detector is synchronized. The return value is in Hz.
- setup(patt_type: Literal['DATA', 'PRBS'] = None, patt_len: int = None, prbs: Literal[7, 9, 11, 15, 23, 31] = None, data: str | ndarray = None, eye_threshold: float = None, center_delay: bool = False, center_offset: bool = False, offset_mV: float = None, delay_ps: float = None, sync_threshold: float = None, sync: bool = None, run: bool = None, stop: bool = None, CHs: int | list[int] = None)[source]
Configure the PED with the specified parameters in a sequential and logical order.
This method allows setting up the physical layer (alignment), the logical layer (pattern/sync), and the measurement state (run/stop) in a single function call.
- Parameters:
patt_type (
str{‘DATA’, ‘PRBS’}, optional) – Pattern type expected by the error detector.patt_len (
int, optional) – Length of the pattern (only relevant ifpatt_type='DATA').prbs (
int, optional) – Polynomial order for PRBS patterns (e.g., 7, 15, 31). Only used ifpatt_type='PRBS'.data (
strornp.ndarray, optional) – Binary data sequence to be programmed into memory. Only used ifpatt_type='DATA'.eye_threshold (
float, optional) – BER threshold used during the auto-alignment process (center_delay/center_offset) to detect the edges of the eye. Default is usually 1e-3.center_delay (
bool, optional) – If True, initiates the Auto-Align Clock Delay process. The instrument scans the horizontal axis to find the center of the data eye (optimal sampling time).center_offset (
bool, optional) – If True, initiates the Auto-Align Voltage Offset process. The instrument scans the vertical axis to find the center of the data eye (optimal sampling voltage).offset_mV (
float, optional) – Manually sets the decision threshold voltage offset in millivolts (-300 to +300 mV).delay_ps (
float, optional) – Manually sets the clock-to-data delay in picoseconds (-50 to +50 ps).sync_threshold (
float, optional) – BER threshold below which the instrument considers the pattern Synchronized. Range: 1e-8 to 1e-1.sync (
bool, optional) – If True, executes the Pattern Synchronization process. The PED shifts its internal reference pattern to match the incoming bit stream.run (
bool, optional) – If True, enables the error counting gate (Start Measurement). Requires successful synchronization.stop (
bool, optional) – If True, disables the error counting gate (Stop Measurement).CHs (
intorlist[int], optional) – Specific channels to configure. If None, applies to all channels.
Notes
Difference between Alignment and Synchronization:
To measure BER correctly, the PED must perform two distinct operations:
Alignment (Physical Layer - ``center_delay``, ``center_offset``):
The instrument adjusts the sampling point (time and voltage) to position it in the center of the “Eye Diagram”.
Without alignment, the PED samples noise or signal edges, resulting in a BER ~0.5.
This process is analog and optimizes the signal quality reading.
Synchronization (Logical Layer - ``sync``):
The instrument shifts the bits of its internal reference pattern to match the sequence of the incoming data stream.
This happens after alignment. If the signal is not aligned (sampling noise), synchronization will fail.
Successful sync forces the BER to 0 (or very low values) assuming the link is healthy.
Execution Order:
When multiple parameters are passed, this method executes them in the following order to ensure stability:
Pattern Configuration (Type, PRBS/Data)
Alignment Thresholds (Eye Threshold)
Physical Alignment (Center Delay -> Center Offset -> Manual Values)
Synchronization Configuration (Sync Threshold, Type)
Execution of Synchronization (Sync)
Gating (Run/Stop)
Examples
Full setup sequence: Configure PRBS31, align the eye, sync the pattern, and start measuring.
>>> ped = PED4002('USB0::...') >>> ped(patt_type='PRBS', ... prbs=31, ... center_delay=True, # Find horizontal eye center ... center_offset=True, # Find vertical eye center ... sync=True, # Lock pattern ... run=True) # Start counting errors
- class opticomlib.lab.IDPhotonics(host='192.168.0.1', port=2000, timeout=0, usb=False)[source]
Minimal SCPI driver for IDPhotonics lasers
Attributes
Use USB connection (True) or Ethernet (False).
IP address of the device.
Port for socket or USB connection.
PySerial object instance (if usb=True).
Socket object instance (if usb=False).
Main methods
__init__([host, port, timeout, usb])wavelength(wavelength[, ch])sets the wavelength of the laser in nm, at the specified channel
get_wavelength([ch])returns the current wavelength of the laser in nm, at the specified channel
power(power[, ch])sets the power of the laser in dBm, at the specified channel
get_power([ch])returns the current power of the laser in dBm, at the specified channel
fine_tune(offset[, ch])fine tunes the laser frequency in GHz, at the specified channel
output(value[, ch])Enables or disables the output of the laser at the specified channel.
close()Close connection
- usb = False
Use USB connection (True) or Ethernet (False).
- host = '192.168.0.1'
IP address of the device.
- port = 2000
Port for socket or USB connection. If usb=True, this is the COM port number.
- serial = None
PySerial object instance (if usb=True).
- socket = None
Socket object instance (if usb=False).
- get_wavelength(ch=1) float[source]
returns the current wavelength of the laser in nm, at the specified channel
- wavelength(wavelength: float, ch=1)[source]
sets the wavelength of the laser in nm, at the specified channel
- get_power(ch=1) float[source]
returns the current power of the laser in dBm, at the specified channel
- output(value: bool, ch=1)[source]
Enables or disables the output of the laser at the specified channel. To enable all lasers use ch=’*’. This method wait until output power is stable.
- __call__(wavelength: float = None, power: float = None, output: bool = None, ch: int = 1)[source]
Convenience method to set wavelength and power in a single call.
- class opticomlib.lab.LeCroy_WavExp100H(addr_ID: str = None, timeout_ms: int = 10000)[source]
LeCroy Wave Expert 100H - minimal, extensible VISA wrapper for Teledyne LeCroy MAUI/XStreamDSO scopes adquisition.
Attributes
instMain methods
__init__([addr_ID, timeout_ms])run()Run acquisition again
stop()Stop any ongoing acquisition.
single()Arm the scope for a single acquisition.
autoset()Run AutoSetup on the oscilloscope (convenience wrapper).
acquire_waveform([ch, points, sweeps])Acquire waveform data from the specified channel.
close()Close the connection to the instrument.
Basic workflow example
>>> scope = LeCroy_WavExp100H(addr_ID) >>> t, v = scope.acquire_waveform(ch=1) >>> scope.close()
- acquire_waveform(ch: str = 'C1', points=None, sweeps: int = 1)[source]
Acquire waveform data from the specified channel.
- Parameters:
ch (str) – Channel to acquire from {‘C1-4’, ‘F1-8’}.
points (int, optional) – Number of points to acquire. If None, acquires all available points.
- Returns:
t (np.ndarray) – Time array corresponding to the waveform samples.
v (np.ndarray) – Voltage array of the acquired waveform.
- class opticomlib.lab.EXFO_FVA60B(port, timeout=11)[source]
Driver for EXFO FVA-60B Variable Attenuator.
Main methods
__init__(port[, timeout])Initializes the connection with the EXFO FVA-60B attenuator.
attenuation(db_value)Sets the attenuation.
Reads the current attenuation.
wavelength(wavelength)Sets the wavelength.
Executes calibration (zeroing).
Reads the current insertion loss.
close()Close the connection to the instrument.
- __init__(port, timeout=11)[source]
Initializes the connection with the EXFO FVA-60B attenuator. Configuration according to manual: 9600 baud, 8 bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
- Parameters:
port (str) – Serial port where the FVA-60B is connected (e.g., ‘COM3’ or ‘/dev/ttyUSB0’).
timeout (int, optional) – Timeout for reading in seconds. Default is 11 seconds.
- get_attenuation()[source]
Reads the current attenuation. Command: >?<. Returns float with the value in dB.
- attenuation(db_value)[source]
Sets the attenuation. Command: >A-xx.xx<. Note: The manual indicates that the value must be divisible by 0.05 dB.
- wavelength(wavelength)[source]
Sets the wavelength. Command: >Lxxxx<. According to the manual, the range is 1270 to 1330 nm with a 10 nm step.